Prostatitis Symptoms And Treatments Overview By Canadian Family Pharmacy

On this page:
In this survey, Canadian Family Pharmacy specialist will talk about the most widespread prostate diseases in men, and a brief overview of treatments available online through Canadian Pharmacy service mycanadianfamilypharmacy.com.
Acute and chronic prostatitis summary
Acute prostatitis is a sudden inflammation of the prostate gland caused by bacteria. The trouble begins with partial severe Pain in the area between the penis and rectum openings. The Pain radiate to the stomach or back to the back. You often get fever, chills and impaired general condition. Other symptoms may include pain in the bowel duct, painful and frequent water vents, weak urine tract, overfill of urinary bladder and possibly also relapses. Acute bacterial prostatitis is a relatively rare disease.
Bacterial infection in the gland leads to local inflammation. In most cases, the bacteria are now assumed by the urethra, or through the intestinal lymphatic system. The diagnosis is made in the light of the typical symptoms mentioned above, and examination of the patient. The doctor examines the prostate by feeling it with a rectum in the rectum. The bladder may also feel over the stomach if it is overfilled. In addition, urine and blood samples are taken.
This is a bacterial infection and therefore antibiotic treatment is recommended. Different types of antibiotics can be used and treatment for two weeks is recommended. Included patients may need antibiotics intravenously in hospitals, while less ill patients receive a tablet cure as they take home. In the case of an overblown bladder, the bladder must be emptied using a catheter directly in the bladder.
If treatment with antibiotics does not help, an ultrasound examination of the prostate should be performed to determine whether there is a prostatic abscess (abscess). Prostate abscesses are very rare, but the symptoms are reminiscent of acute prostatitis in the initial phase. Most people get fast with antibiotic treatment, and the forecast is good. In rare cases, complications may occur in the form of blood poisoning. Persistent prostatitis can rarely lead to recurrent urinary tract infections and sterility.
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is a persistent inflammation with pain in the small pelvis. Pain located to the perineum (the area between the rectum opening and the scrotum), which can radiate against the scrotum, groin, inside of the thighs, lumbar spine and lower abdomen. The most common form of chronic prostatitis is non-bacterial and the cause has not yet been clarified. Diagnosis is made according to the patient’s history of illness.
So-called NSAIDs can alleviate symptoms. Chronic prostatitis often passes by itself.
Chronic prostatitis is a persistent inflammation with pain in the small pelvis. The process is often long-term. Chronic prostatitis or, as it should be referred to, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a very common condition (in 5-10% of the male population). The limit to normal inconvenience may be vague.
The cause of the non-bacterial (chronic pelvic pain syndrome) variant characterized by more continuous Pain in the small pelvis has not been clarified. Much suggests that it may be a hypersensitivity / cramp in the pelvic muscles that lies behind the Pain. This non-bacterial variant is the most common form of chronic prostatitis.
There is a more unusual variant “bacterial prostatitis” where bacteria can be detected in the urine and where the affected man does not have perineum Pain but more acute symptoms as in a urinary tract infection. Cooling can be a triggering factor and almost always aggravates also the symptoms (chronic pain) of chronic prostatitis. Stress and prolonged sitting can also aggravate the situation.
The diagnosis is based on the patient’s history of illness. Prostate and pelvic floor muscles can be examined with a finger in the rectum of the patient. Sensitivity and pain in the investigation strengthen the diagnosis. In the event of problems with emptying the bladder, it may be appropriate to conduct a more extensive examination of the urethra and the bladder.
The result of the investigation may give one of the following diagnoses:
- Bacterial prostatitis – bacteria detected.
- Non-bacterial (chronic pelvic pain syndrome).
Heat usually always relieves the symptoms. Cooling, long-term sitting and cycling should be avoided. So-called NSAIDs can alleviate symptoms. They are anti-inflammatory and analgesic. In the case of bacterial prostatitis (with bacteria in the urine) antibiotic treatment may be relevant.
The following investigations will be ordered by doctor in order to confirm the diagnosis:
- Urine tests show white and red blood cells.
- Urinary cultivation to end urinary tract infections.
- Rectal examination of the prostate to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other diseases.
- Blood cultivation in severe acute prostatitis.
- Repeat prostate secretion cultivation to capture the type of bacteria or fungus and what treatment is needed.
- STD tests.
- PSA is taken in suspected prostate cancer in prostate palpation.
- Cystoscopy examination (looking into the urethra with a camera) to stop the urinary tract obstruction, obstruction of the ejaculation channel sensation and other changes in the prostate and bladder.
- TRUL (ultrasound prostate examination by rectum) to stop prostate abscess, cysts, calcification, reproductive organs and cancer.
- TRUL + Biopsy (ultrasound prostate and cell sampling) to stop prostate cancer and confirm prostate diagnosis.
- Magnet radius pelvis to end the change in the pelvic organs and skeletons.
Avoid what causes prostate, other lifestyle, start doing relaxation exercises. Anti-inflammatory drugs function as pain relief and swell of the prostate. Antibiotics in bacterial prostatitis after cultivation and resistance determination to provide the right antibiotics. Also, can be given to non-bacterial prostatitis to access those organisms that we can not grow. Antibiotics treatment often results in more than 40% of patients (but it may be anti-inflammatory or placebo).
Alfa blockers help to relax the muscles of the prostate and urinary bladder, which relieves the symptoms. Prostate massage has a role in non-bacterial prostatitis treatment. The massage is done with special techniques to not damage tissues and worsen the condition. The massage clears the secretion stuck in the prostate gland, reduces internal pressure in the prostate and relieves the symptoms. It can be done 2-3 times per week for 2-3 weeks and for some long lasting pain relief.
Finastrid and Avodrat have proven to have a mild effect on the severely treated prostatitis (even in patients with low prostate volume) but side effects (losing sex, ED, breast enlargement and aches) often lead to the patient discontinuing taking the medicine.
ESVT (Electromagnetic shockwave treatment) shows very good results for the treatment of CPPS. It helps to minimize the intensity and frequency of chronic pelvic pain. The mechanism is not clear but the greatest probability is related to the increased blood flow in the prostate and pelvic muscle. Which is the case with most research results. It helps the healing process in the nerve and muscle damage as a stage in the inflammation and decreases the prostate and pelvic muscle spasms.
Antidepressants help in chronic prostatitis when suffering from anxiety and depression of chronic pain and fear of cancer.
Treatment is safe, simple, painless. There are 6 treatments given for 3 weeks (2 times / week) each treatment takes 30 min. Treatment may be repeated after 3 months if necessary. Heat treatment Man burns or boils the prostate gland and its internal nerves with high energy radio waves or microwaves that produce high heat in the prostate. The method is used in cases with very severe inconvenience and does not respond to the above treatments.
Surgery appointed for prostatitis is of several types:
Radical resection is only done in highly difficult bacterial prostatitis that has not improved with all treatment methods mentioned above. Requires the patient to complete his family planning. After surgery, you can not get children because the spinal fluid enters the bladder after surgery.
The course is often varied by week to month-long forest with more pronounced inconvenience in winter. The condition can affect both working life and leisure but does not cause permanent damage and does not increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. Chronic prostatitis often passes by itself.
It is common for the symptoms to recur. Call your healthcare provider if the prostate is very large, a slow urine flow through the urethra may cause a backflow of urine to the kidneys, which can cause kidney damage; if the urine flow stops completely, it is considered an emergency. Seek medical help if you suspect that you have symptoms of chronic prostatitis. Avoiding urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases can reduce the risk of chronic prostatitis. If you are taking antibiotics, finish the entire cure of antibiotic treatment to reduce the risk of the condition back.
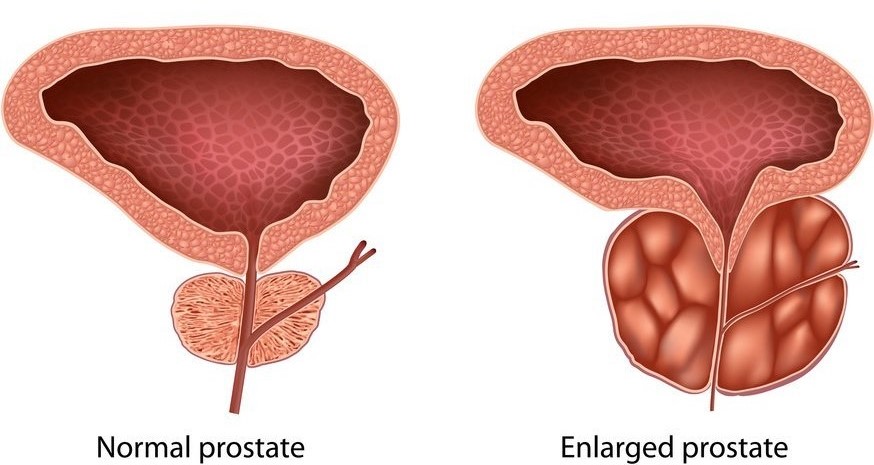
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms and treatments
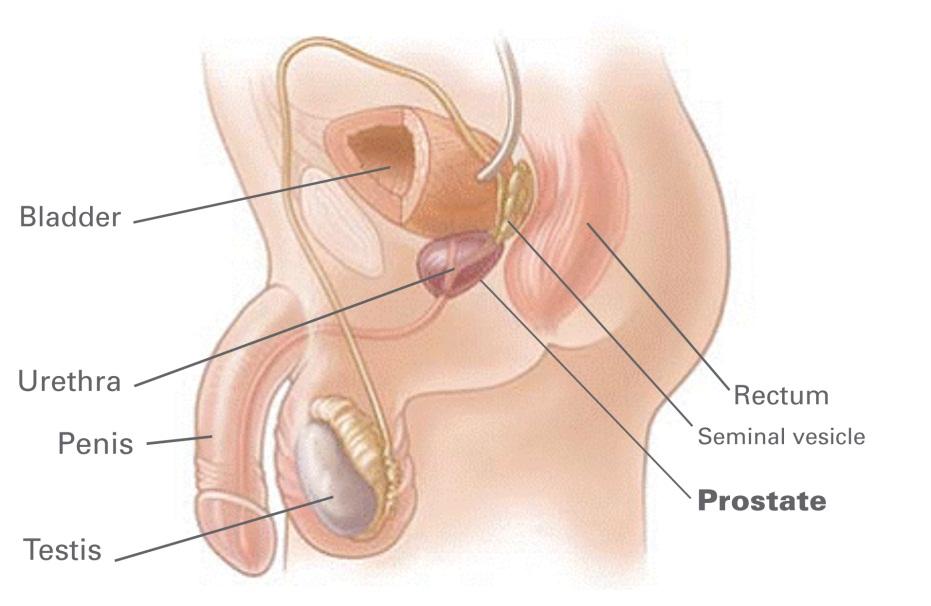
Prostate is a male reproductive gland that produces the fluid that transports sperm during ejaculation. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine passes out of the body. An enlarged prostate means that the gland has become larger. Prostate enlargement occurs in almost all men when they grow older. As the gland grows, pressure on the urethra can cause urinary problems and problems with the bladder. An enlarged prostate is often called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It is not cancer, and it does not increase your risk of prostate cancer.
Some facts about prostate enlargement:
- The likelihood of developing an enlarged prostate increases with age
- BPH is so common that it has been said that all people will get an enlarged prostate if they live long enough
- A small magnification of prostate occurs in many men over 40 years and more than 90% of men over 80 years
- No risk factors have been identified other than normal functioning testicles
Less than half of all men with BPH have symptoms of the disease, which include:
- Dripping at the end of urination
- Inability to urinate (urinary retention)
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Incontinence
- Need to urinate two or more times a night
- Pain in urination or bloody urine (these may indicate infection)
- Delayed start in urinary flow
- Effort to urinate
- Strong and sudden need to urinate
- Weak urine radius
After taking a full medical history, your doctor will perform a digital rectal examination to feel the prostate gland. The following tests can also be performed: urine flow; post-residual urine test to see how much urine remains in the bladder after urination; pressure-flow studies to measure the pressure in the bladder while kissing, urine analysis to look for blood or infection, urinary cultivation to control infection, Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) blood sample to detect prostate cancer, cystoscopy. Additionally, you may be asked to fill out a form to evaluate the degree of symptoms and their impact on your daily life. Your score can be compared to previous registry checks if the condition gets worse.
The choice of treatment is based on the severity of the symptoms, the extent to which they affect your daily life, and the occurrence of other disease. Treatment options are lifestyle changes, medication or surgery. If you are over 60, you are more likely to have symptoms. However, many men with an enlarged prostate have only mild symptoms. Self-care is often enough to make you feel better. If you have BPH, you should have an annual degree to monitor the development of your symptoms and determine whether any change in treatment is necessary.
The self care for mild symptoms consists in the following steps: peek when you first get in touch; go to the toilet when you have the chance, even if you do not feel a need to urinate; avoid alcohol and caffeine, especially after dinner; do not drink much fluid at once; spread out the fluid intake throughout the day. avoid drinking liquids within 2 hours of bedtime; avoid taking prescription free cold and sinus medicines containing antihistamines; these drugs may increase BPH symptoms; keep warm and exercise regularly; cold weather and lack of physical activity can exacerbate the symptoms; perform kegel exercises (pelvic exercises); Reduce stress: nervousness and tension can lead to more frequent urination.
Alfa-1 blockers (doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin, terazosin, and afluzosin) are a class of drugs also for the treatment of hypertension. These drugs relax the muscles of the blue neck and prostate. This makes it easier to urinate. Most people treated with alpha-1 blocker experience that it helps. Antibiotics can be prescribed to treat chronic prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), which may accompany BPH. Some men notice relief of their BPH symptoms after a cure of antibiotics.
Many herbs have been tested for the treatment of enlarged prostate. Saw Palmetto has been used by millions of people to relieve the symptoms of BPH and is often recommended as an alternative to medication. Some studies have shown that it helps with symptoms, but there is evidence that this popular herb is no better than an inactive pill for relief of signs and symptoms of BPH. Additional studies are required.
Transurethral Prostatic Resection (TURP): This is the most common and most proven surgical treatment of BPH. TURP is performed by inserting an instrument through the penis and removing the prostate bit by piece. Transurethral incision of prostate (TUIP): This procedure is similar to TURP, but is usually in men who have a smaller prostate
It is usually performed without the need for a hospital stay. TURP is a range through the penis until the prostate is reached. Then, instead of removing the prostate, a small incision is made in the prostate tissue to enlarge the opening of the urethra and the bladder outlet.
Simple prostatectomy: An open prostatectomy is usually performed using general or spinal anesthesia. An incision is placed through the abdominal wall or perineum (area behind the scrotum). Only the inner part of the prostate gland is removed. The outer part is left. This is a lengthy procedure, and it usually requires a hospital stay of 5 to 10 days. Most men who get prostate surgery have better urine flow and improved symptoms.
Patients who receive these minor procedures are more likely to need surgery again after 5 or 10 years.
However, these procedures can be a choice for:
- Younger men (many of the minor interventions imply a lower risk of impotence and incontinence than TURP, although the risk of TURP is not very high)
- Elderly patients
- Patients with severe medical conditions including uncontrolled diabetes, cirrhosis, alcoholism, psychosis, and severe lung, kidney or heart disease
- Men who take anticoagulants
Robot-guided prostatectomy is another newer technology. However, the technology is not widely available, and the surgeon experience should be considered. In addition, there are no long-term studies of this operation.
Men who have had long-term BPH with a gradual increase in symptoms may develop: sudden inability to urinate, urinary tract infections, urinary stones, injuries to the kidneys, Blood in the urine. Even after surgical treatment, a repeat of BPH may develop over time.
Call your doctor immediately if you have:
- Less urine than usual
- Fever or chills
- Blood or urine
Also, call your doctor about: the bladder does not feel completely empty when you urinate; you are taking medicines that can cause urinary problems such as diuretics, antihistamines, antidepressants, sedatives or sleep aid.
Prostate drugs at Canadian Family Pharmacy
Finasteride is a medicine used in benign prostatic enlargement. It belongs to the drug group 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and the active substance is finasteride. At Canadian Family Pharmacy mycanadianfamilypharmacy.com, Finasterid is available as tablets in the strength of 5 milligrams. The medicine is prescription. Dihydrotestosterone, which is the active form of the male sex hormone testosterone, is needed for the prostate gland’s normal function and growth. It is formed in the prostate gland by the enzyme 5-alpha ductuctase. Finasteride inhibits this enzyme so that it forms less dihydrotestosterone, which causes the prostate gland to decrease. As a result, urine flow can be improved and the risk of failure to pee reduces. The best effect is if the prostate gland is large from the start. When stopping the drug, the prostate gland begins to grow again, and the symptoms may then return.
 You should swallow the whole tablet with some water. The tablet may not be divided or crushed. When a medicine is printed on prescription, the dose is adjusted for the person to use the medicine. Therefore, it is important to follow the dosage instructions on the label on the packaging. A regular dose is a tablet, 5 milligrams per day as a single dose. If you forget to take a tablet, skip the missed dose and take the next dose as usual, the next time it is time.
You should swallow the whole tablet with some water. The tablet may not be divided or crushed. When a medicine is printed on prescription, the dose is adjusted for the person to use the medicine. Therefore, it is important to follow the dosage instructions on the label on the packaging. A regular dose is a tablet, 5 milligrams per day as a single dose. If you forget to take a tablet, skip the missed dose and take the next dose as usual, the next time it is time.
Tablets that have been broken should not be handled by women who are or may be pregnant. The active substance can be absorbed through the skin and affect the development of the fetus. Some of the men who use finasteride may have reduced sex drive, impotence, depressedness or loosening of the larynx. In most cases, this goes back when you stop taking the medicine. If you get side effects that are difficult, consult your doctor. You may then need some other form of treatment.
There are other medicines that contain finasteride. It may be good to know that you do not accidentally use several medicines that contain the same active substance, because you can get too much. Examples of medicines containing finasteride are Proscar. There is also another drug, Propecia, which contains a lower dose of the active substance finasteride and has a different application. There are other medicines that work in the same way that you should not use with Finasterid, for instance, Avodart. Before taking any of the drugs mentioned above, it is important to consult a trusted healthcare specialist.